 thanassis.com
thanassis.comMy other sites |
| The Object Model Creating and Using Objects Example of a Class and its Instance Constructors Methods Calling Methods Inheritance Inheritance Example Abstract Interfaces |
|
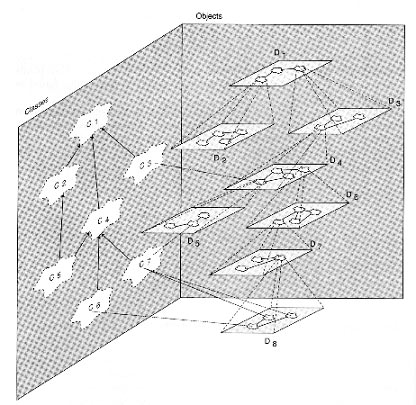 |
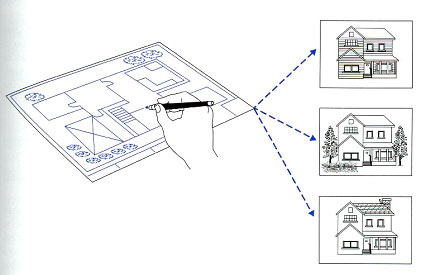
Is a view of the world in terms of Objects and their
relationships Why we need it ? |
 |
To create a custom object in Java we need to: - Create its class - Instantiate an object from the class using : new |
 |
class Star {
}
public class TestStar {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
Star my_star;
my_star = new Star() ;
}
}
|
 |
class Star {
int edges;
public Star(int _edges) {
edges=_edges;
}
}
public class TestStar {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
Star first_star,second_star;
first_star = new Star(5) ;
second_star = new Star(7);
}
}
|
 |
class Star {
//state, data
int edges_num=3;
//methods, behaviour
public Star(int _edges) {
edges_num =_edges;
}
public void setEdges(int _edges){
edges_num=_edges;
}
public int getEdges() {
return edges_num;
}
}
Is the constructor a method? |
|
public class TestStar {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
Star first_star,second_star;
first_star = new Star(5) ;
second_star = new Star(7);
first_star.setEdges(10);
second_star.setEdges(14);
System.out.println("1st Star:" + first_star.getEdges());
System.out.println("2nd Star:" + second_star.getEdges());
}
}
|
 |
|
|
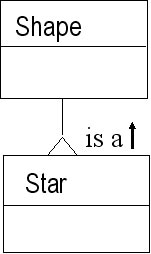
A class can..
specialise, extend, subclass, or be a child of another class. Do you know other terms? |
 |
class Shape {
protected int edges_num;
}
class Star extends Shape {
Star(int _edges) {
edges_num = _edges;
}
}
public class TestStar {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
Star my_star;
my_star = new Star() ;
}
}
|
|
Abstract classes :
cannot be instantiated Abstract methods : 1. cannot have any implementation 2. need implementation from their children |
abstract class Shape {
protected int edges_num;
abstract void draw();
}
class Star extends Shape{
Star(int _edges) {
edges_num = _edges;
}
public void draw() {
}
}
|
|
- are special kinds of abstract classes
- cannot have any implementation - must be implemented by the classes that use them - cannot be compared with C++'s multiple inheritance - sometimes they are used to "tag" instances - usually have an -able ending (Cloneable, Drawable etc) |
interface Drawable {
public void draw() ;
}
class Star extends Shape
|